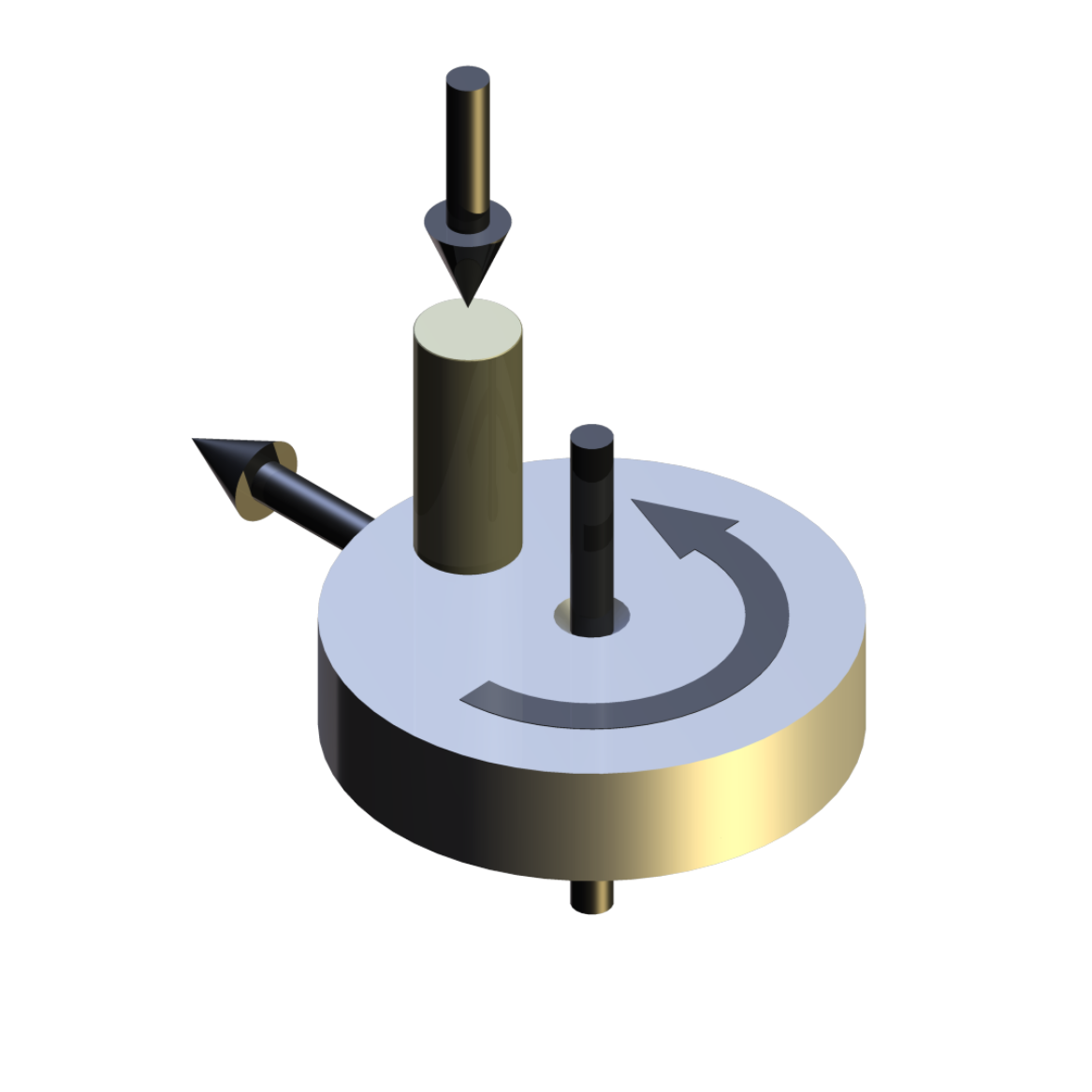
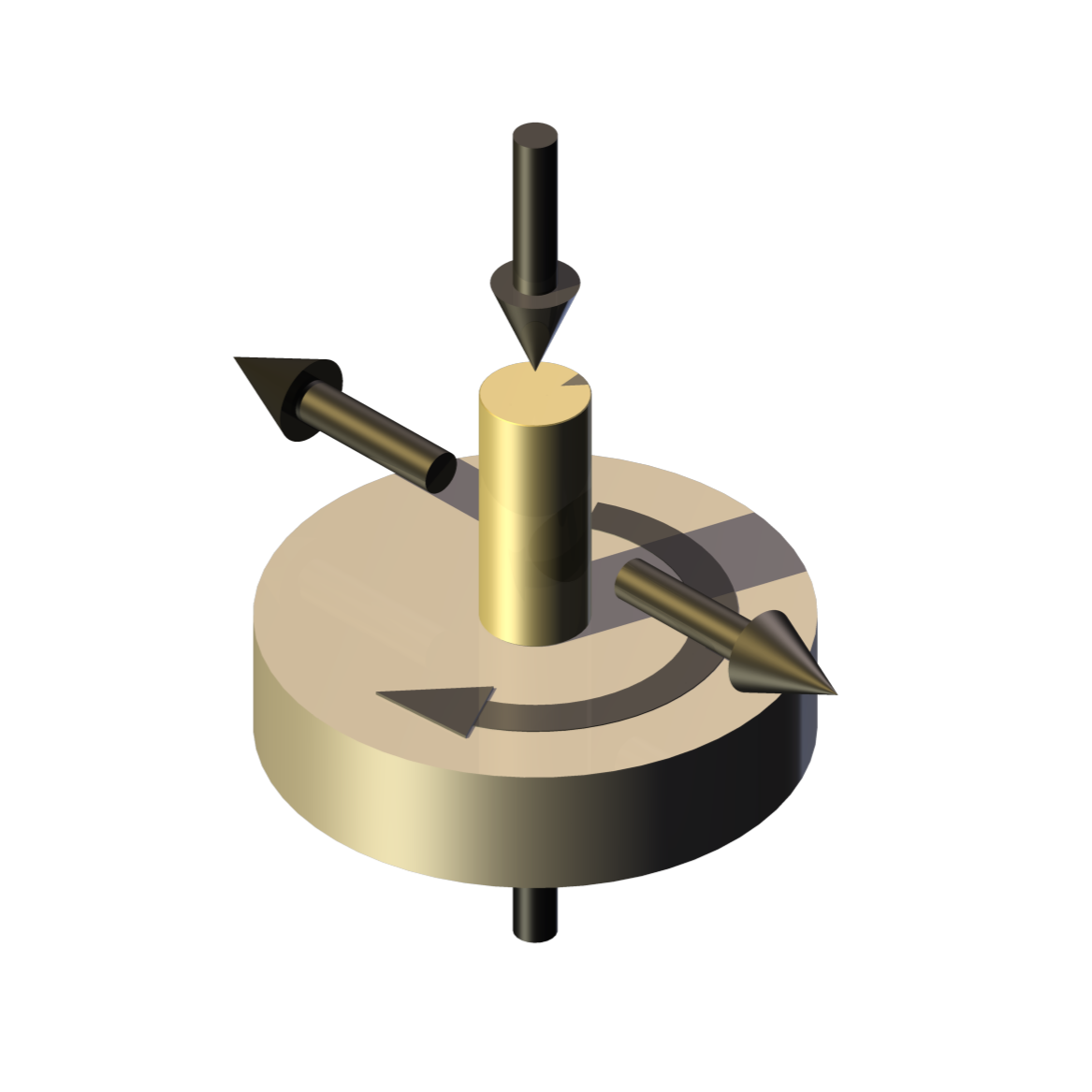
Description
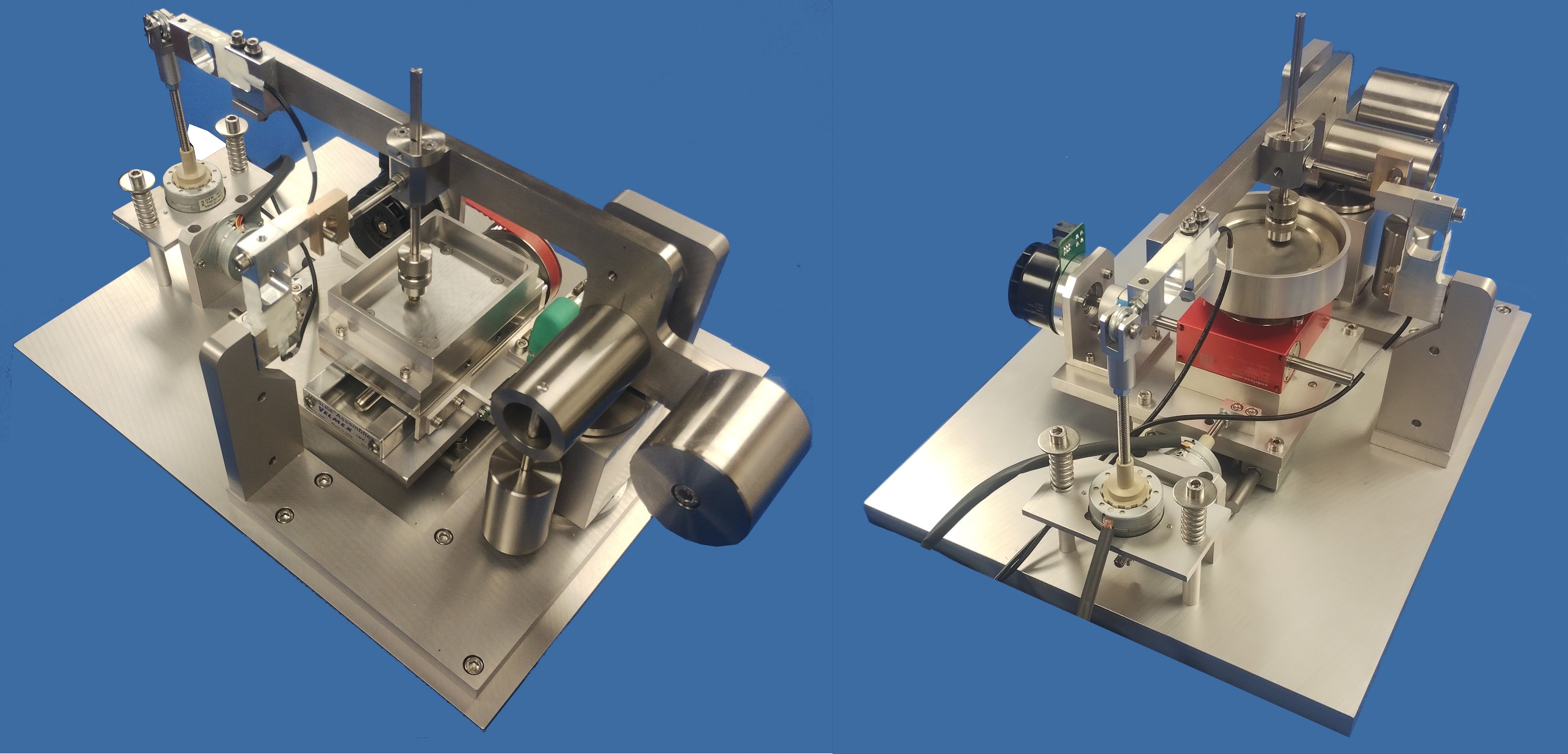
The TE 79 Multi-Axis Tribometer is for friction and wear testing under moderate loads in pin or ball on rotating disc or reciprocating plate configurations. In pin on disc mode the machine complies with ASTM G 99 and DIN 50 324. In both modes, the indexing capability allows tests to be performed in accordance ASTM G132, which requires indexation of the pin, so that it is always presented with a fresh abrasive surface.
TE 79 Base Unit
This comprises the loading and friction force measurement system mounted on a base plate, control hardware, USB interface unit and control software. The machine is bench-top mounted and includes a transparent enclosure and ambient humidity and temperature sensor. The fixed pin or ball sample is carried on a trunnion and gimbal mounted beam. This is counterbalanced to give a neutral balance and to bring the centre of gravity onto the contact plane. Load is applied by ball-screw actuator, with a force transducer for load measurement. The actuator can be used to lower and lift the pin or ball specimen, in and out of contact. This allows tests to be run with programmed dwell time between load application and start of motion. This dwell period is an important parameter in determining the starting friction in elastomeric contacts.
The loading beam is restrained by a strain gauge force transducer in a sliding link, which ensures that only the tangential component of force in the contact (the friction force) is measured, even with the large deflections associated with elastomeric test pieces.
Test modules are mounted on a ball-screw actuator driven cross-slide, allowing plate or disc specimens to be index perpendicular to the direction of sliding.
The unit can be provided with a plastic safety cover, which also acts as a chamber for the user to run under controlled humidity conditions. An ambient temperature and humidity sensor is mounted inside the chamber.TE 79/P Indexing Pin on Disc Module
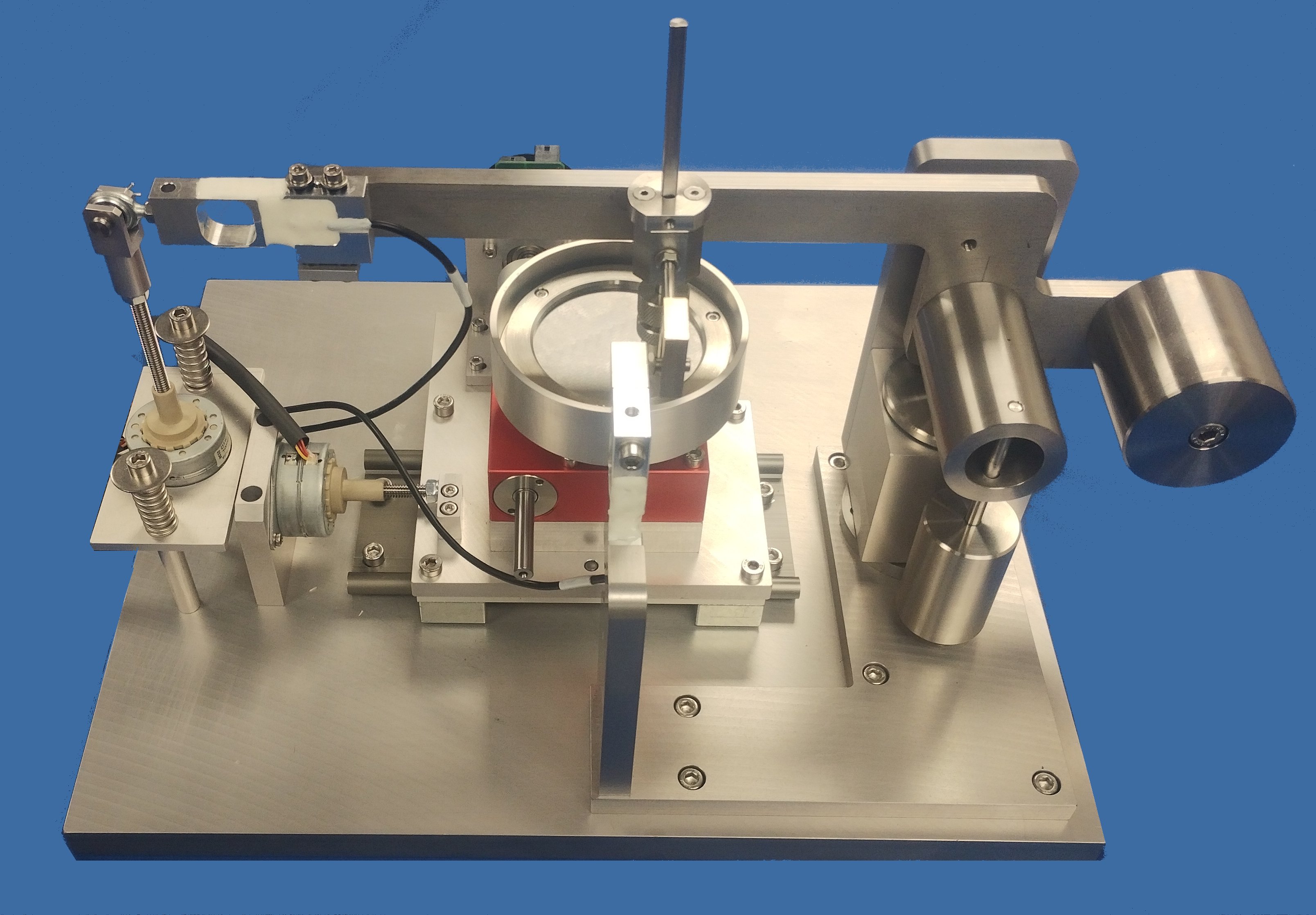
This module comprises a rotating disc assembly mounted on the base unit cross-slide, allowing the pin sample to follow a spiral track on the disc, if required. The disc is driven by a d.c. servo motor. The disc specimen is mounted in a rotating fluid reservoir. The control software may be set to run with a constant rpm or constant velocity during a traverse.
TE 79/H Non-indexing High Temperature Pin on Disc Module

This module allows pin on disc tests to be run at a fixed track radius (hence non-indexing) at temperatures up to 500°C. An electrically powered hot air gun provides the heat source.
TE 79/R Indexing Reciprocating Module
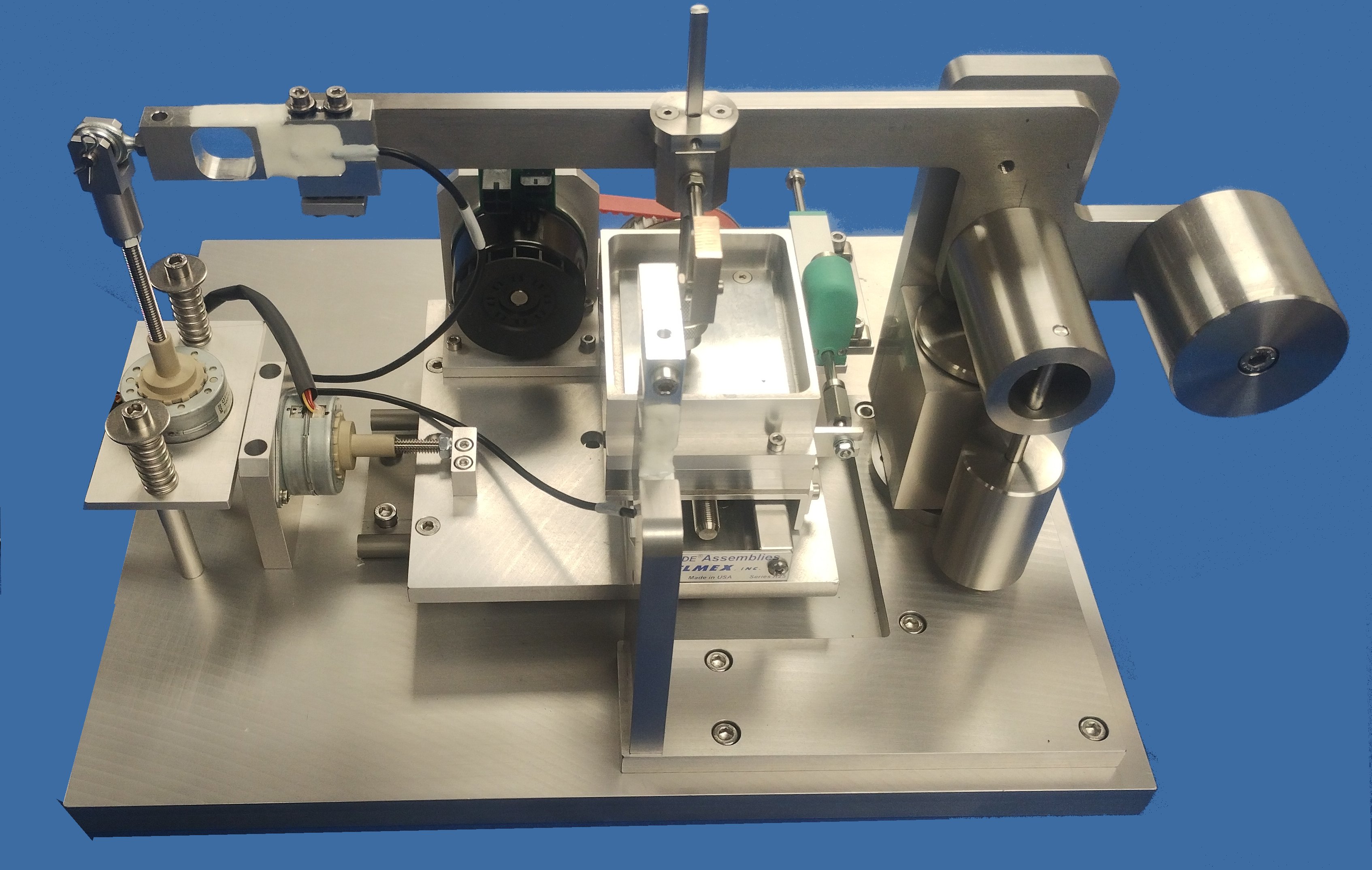
This module mounts on the base unit cross-slide and incorporates a d.c. servo motor driven linear slide, which is used to generate reciprocating motion between the pin or ball specimen and a plate sample. The assembly can be indexed sideways to produce multiple tracks on the same plate specimen, or, for example, a wear track following a rectangular path. The fixture for the lower (moving) specimen includes an electrical resistance heater and a thermocouple for temperature measurement and control.
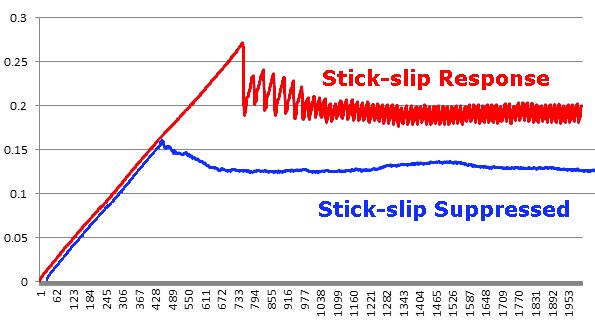
TE 79/R/S Stick-slip Adapter
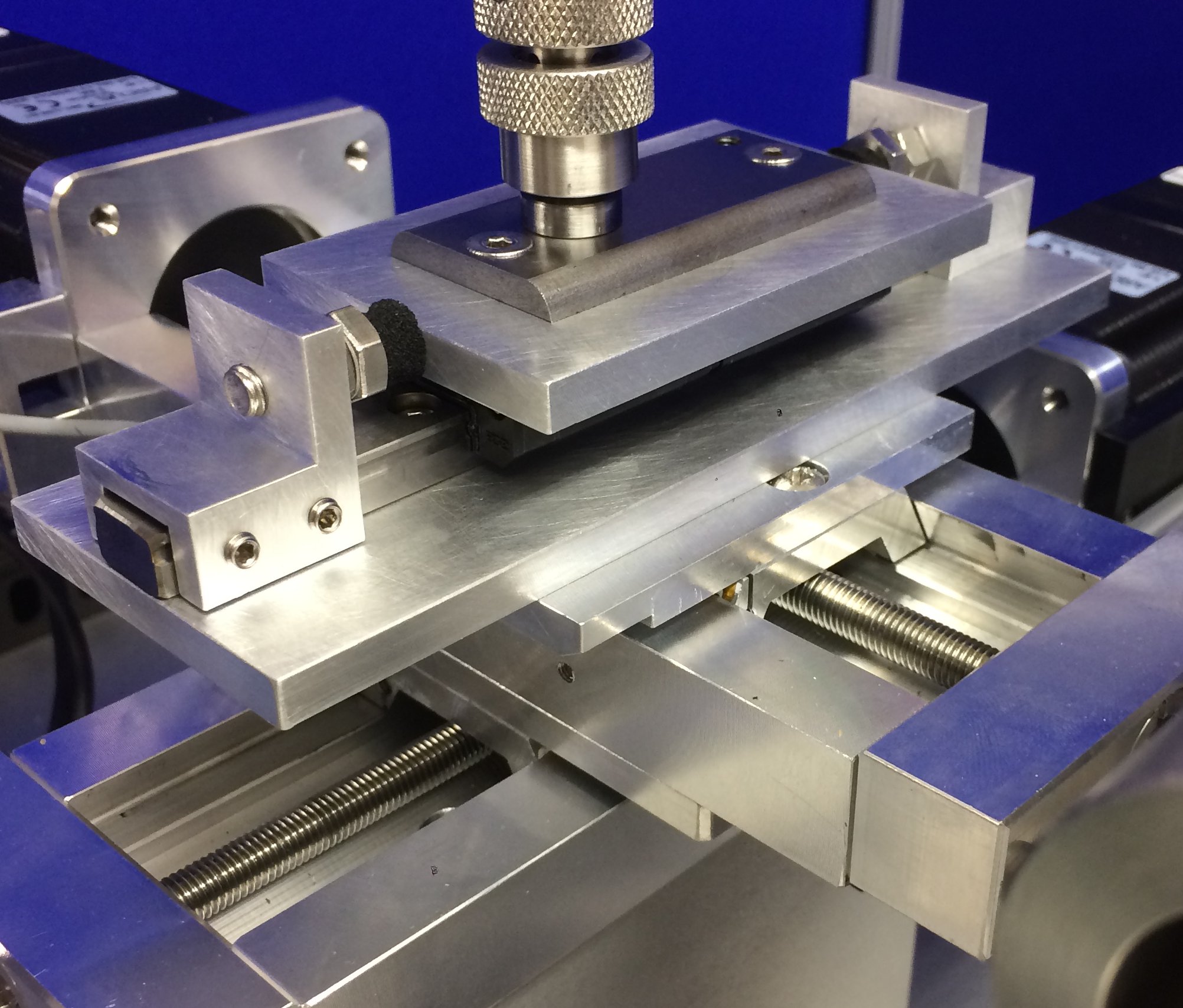

The stick-slip adapter is used in conjunction with the reciprocating module. A plate specimen is supported on a linear bearing, with axial movement constrained either by elastomeric stops or adjustable springs. By adjusting the axial stiffness of the system, the stick-slip response can be tuned. For evaluating a slide-way lubricant, the system is first adjusted to give a stick-slip response, either with a base oil or a poor reference fluid, then tested with the candidate sample, to determine its ability to suppress stick-slip.
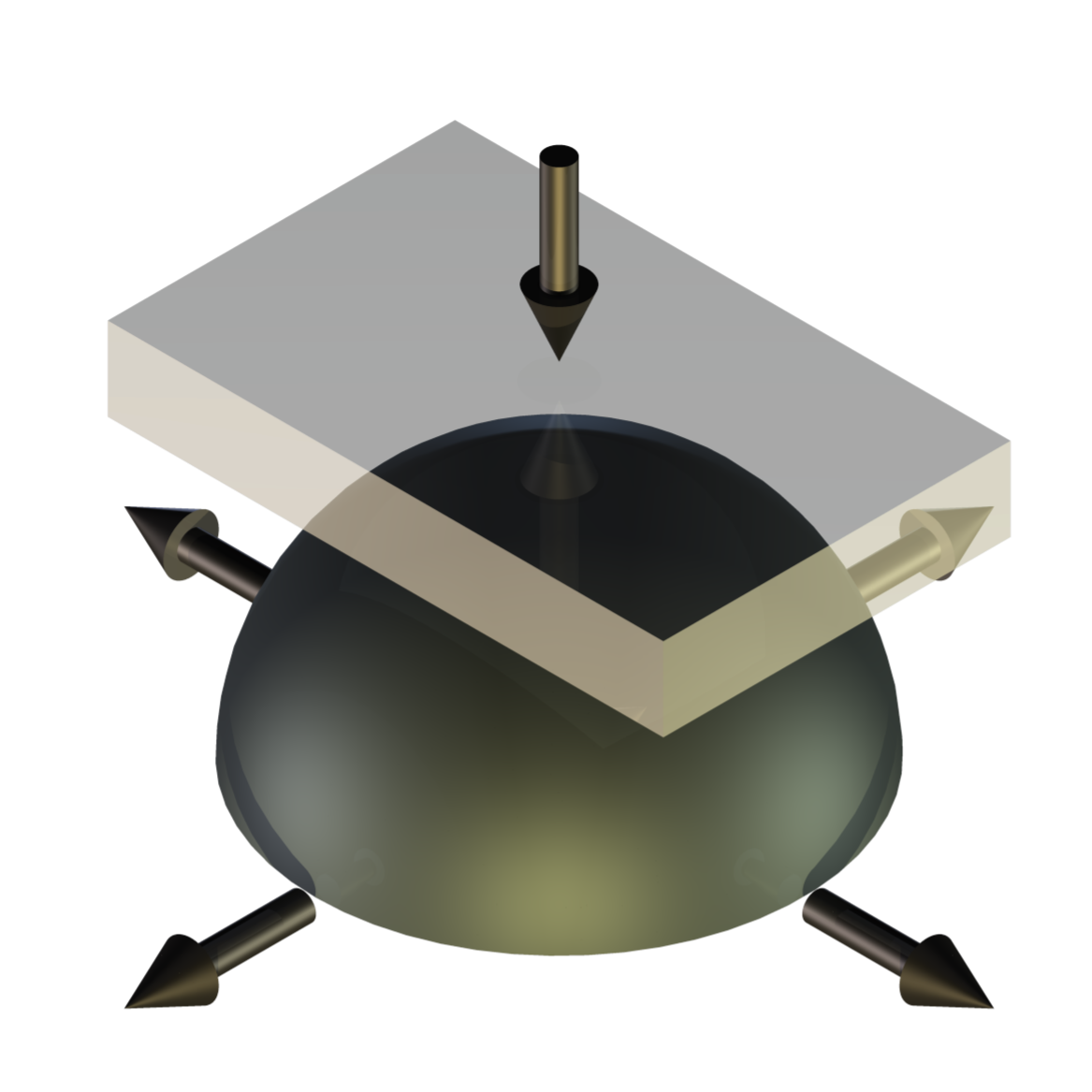
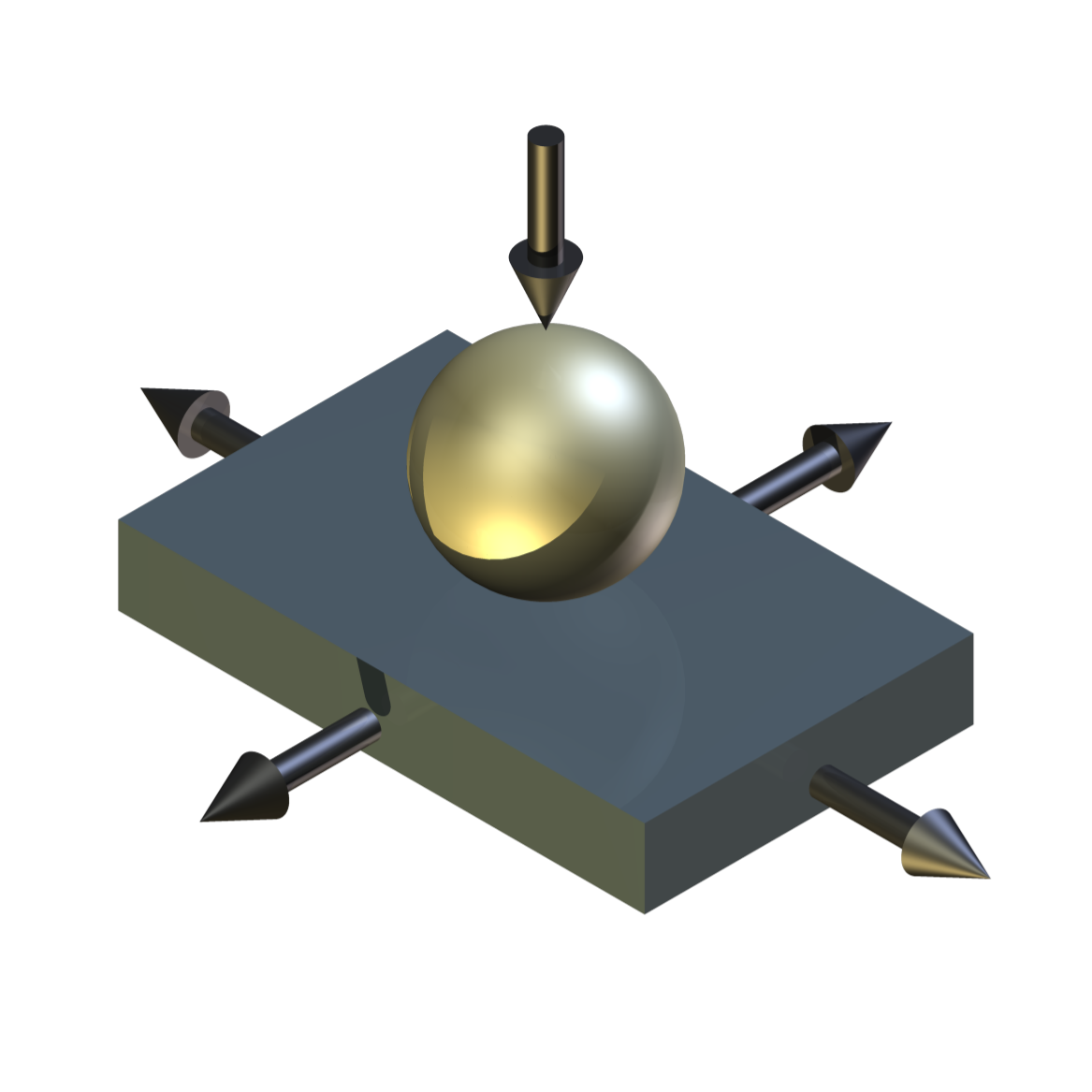
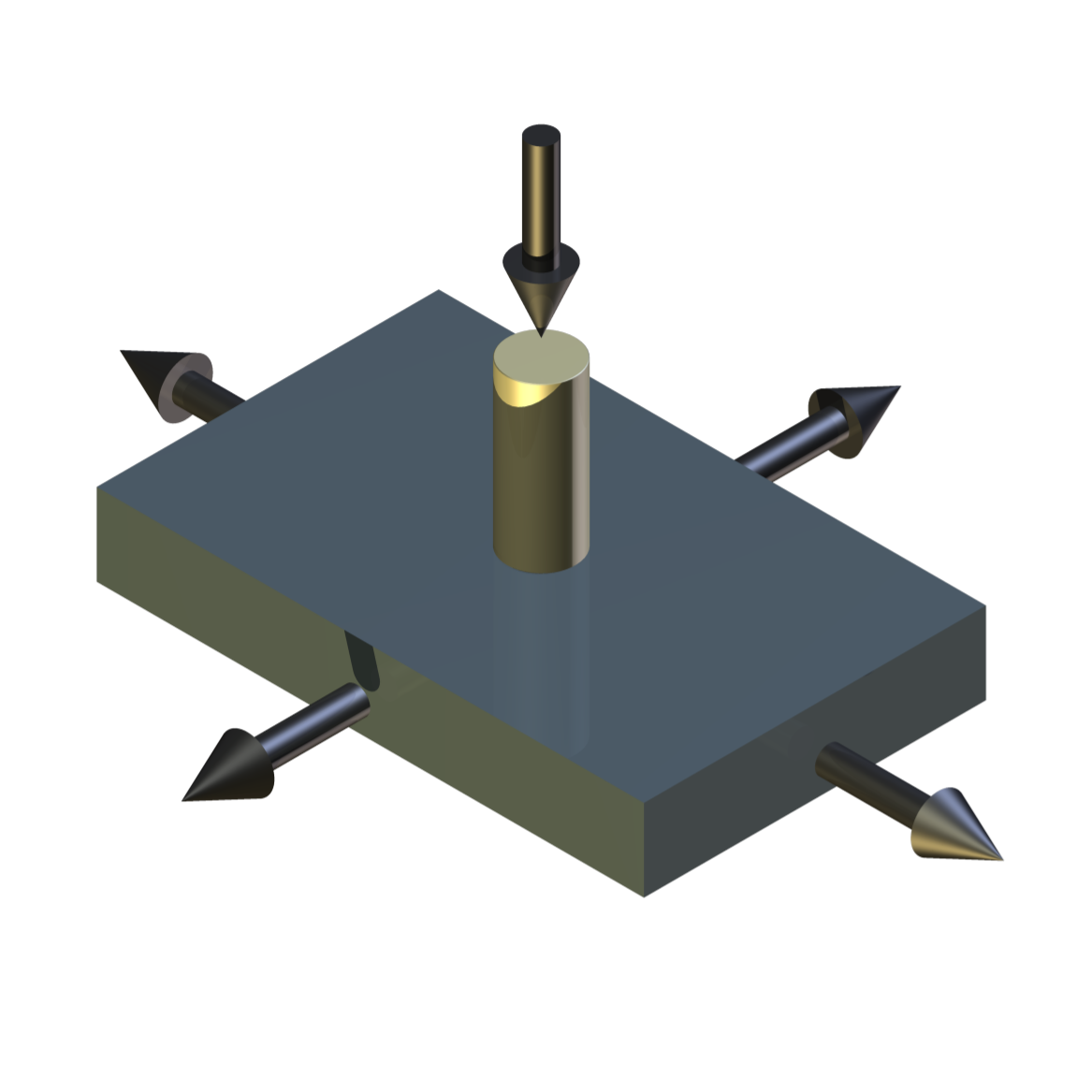
TE 79/R/R Rubber Friction Test Tooling

Based on an original test method developed in collaboration with Rubber Consultants, part of the UK Malaysian Rubber Producers Research Association, the tooling allows tests to be run with contact configurations of ball on rubber flat or plate on rubber hemisphere. With this second configuration, thin rubber sheet samples can be tested, by clamping them over a rubber hemisphere, producing a fully conformal contact. This type of arrangement can also be used to study the friction of cosmetic products, using a suitable sheet material to model human skin.
TE 79/R/C Cooler Pad and Laboratory Chiller
This test assembly replaces the standard fixed specimen heater block in the reciprocating module with a cooler pad. Used in conjunction with a Laboratory Chiller unit with water/glycol mixture as the coolant, temperatures from -25°C to ambient may be achieved. To avoid ice formation, this adapter is best used in conjunction with a simple desiccant dehumidifier system used in conjunction with a controlled air supply.
Control and Data Acquisition
Control and data acquisition are implemented via host PC running COMPEND 2020 Windows compatible software, in conjunction with a Phoenix Tribology USB micro-controller interface.
Automatic control is implemented via user programmable test sequences. Manual control is implemented using on screen toggles. Data is stored to hard disc in either .csv or .tsv file formats.-
Technical Specifications
Contact Configurations: Ball on Flat Pin on Flat Customised Specimens Normal Load: 0.1 to 100 N Load Measurement: Databeam (strain gauge transducer) Friction Force Range: 0 to 50 N Friction Measurement: Databeam (strain gauge transducer) Humidity Sensor: 10 to 90% RH Drive Motor: Brushless d.c. servo motor – 200 W Load Motor: Electric Linear Actuator, 12V dc, 100N Indexing Motor: Electric Linear Actuator, 12V dc, 100N Interface: USB Serial Link Interface Module Software COMPEND 2000 TE 79/P Indexing Pin on Disc Module Contact Configurations: Ball on Disc Pin on Disc Disc Diameter: 100 mm Track Radius: 0 to 40 mm Traverse Speed: 10 mm/min Rotation Speed: 0 to 300 rpm Sliding Speed: up to 1 m/s TE 79/R Indexing Reciprocating Module Contact Configurations: Ball on Plate Plate on Plate Plate on Hemisphere Maximum Sliding Axis Speed: 10 mm/s Maximum Sliding Stroke: 50 mm Maximum Traverse Axis Speed: 1 mm/s Maximum Traverse Stroke: 30 mm Temperature Range: ambient to 100°C Dwell (time delay): User selected in seconds up to 8 hours Temperature Sensor: J-type thermocouple Heating Power: 150 W TE 79/H Non-indexing High Temperature Pin on Disc Module Disc Diameter: 75 mm Track Radius: 0 to 35 mm Temperature: Ambient to 500 °C TE 79/R/C Peltier Cooler Minimum Temperature: -15°C (ambient water cooled) Minimum Temperature: -30°C (chiller water/glycol cooled) RE 79/R/C Laboratory Chiller Working Fluid: 50:50 Water/Glycol Fluid Temperature: -35°C Controlled Parameters Sliding Axis Position (TE 79/R) RPM (TE 79/P) Sliding Axis Speed (TE 79/R) Traverse Position (TE 79/P and TE 79/R) Traverse Speed (TE 79/P and TE 79/R) Temperature (TE 79/R) Dwell Period Test Duration Measured Parameters Sliding Axis Position (TE 79/R) Traverse Position (TE 79/P and TE 79/R) Humidity Ambient Temperature Temperature (TE 79/R) Friction Friction Coefficient Services Electricity: 220/240 V, single phase, 50 Hz, 720 W 110/120 V, single phase, 60 Hz, 720 W Installation Bench-mounting machine: 570 mm x 600 mm x 600 mm high, 40 kg Bench-mounting controller: 530 mm x 530 mm x 240 mm high, 20 kg Packing Specifications: 0.59 m3, GW 120 kg, NW 70 kg -
Machine Overview
Machine Training Video
Stick Slip Tooling
-
Index Tags
-
Call us on +44 (0) 1635 298279
Email : info@phoenix-tribology.com
Email : info@phoenix-tribology.com

