-

Description
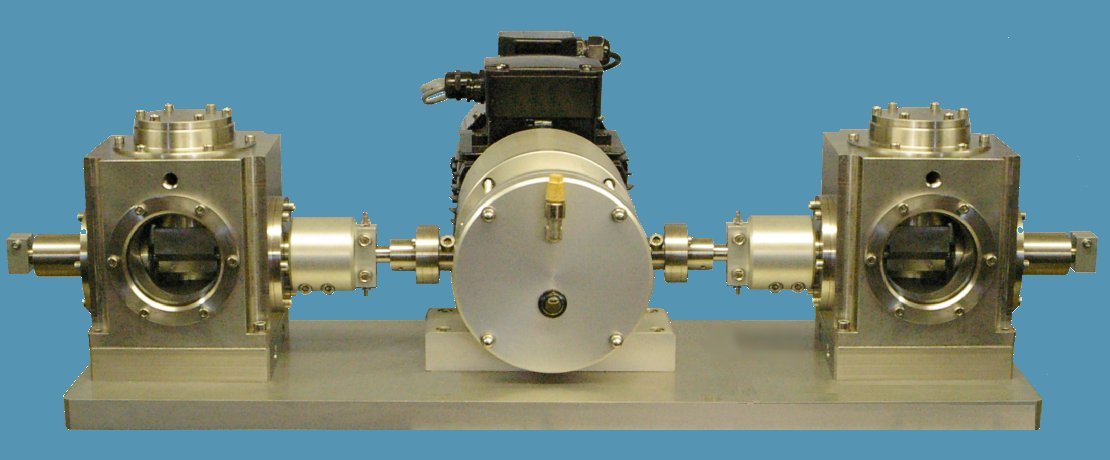
The TE 90 Two Station Fuel Lubricity Wear Test Machine is a pressurised version of the TE 80 Two Station Fuel Lubricity Wear Test Machine. It incorporates two test stations and mounting arrangements for ISO 12156 and ASTM D6079 fuel lubricity test specimens. Load is applied manually by means of dead weights applied directly to the fixed ball specimen carrier.
Machine controls are limited to speed control of the drive motor to give the required frequency, temperature control and test duration. Test data is limited to post-test wear scar measurement only and no facilities are provided for friction force measurement. -
Technical Specifications
Load: Dead Weight Load Measurement: Not available Friction Force: Not available Contact Potential: Not available Pressure: 7 bar maximum Load: 2 N Stroke: 1 mm Maximum Frequency: 50 Hz Temperature: Ambient to 100°C Test Samples: 6 mm diameter ball (point contact) Instrumentation: Speed Indicator Batch Counter Temperature Controllers x 2 Note: Pressurized fluid supply system not included. -
Applications
additive screening boundary lubrication crankcase lubricants diesel fuel lubricity friction modifier fuel lubricity hydraulic fluids multi-station scuffing -
User List
Launched 2011
Shell Global Solutions USA -
Download the Machine Leaflet

