-

Background
The friction and wear performance of wet clutches and other devices of this type can be improved by attention both to the lubricant and the friction material used. In 1995 a Japanese Standard was introduced, describing a method of determining the friction characteristics of various production clutch plate components.
Other test methods include the LVFA and the SAE#2 machines. The former uses small scale parts, manufactured from the friction material, and uses a flywheel coast-down to achieve a full range of sliding speeds. The SAE#2 machine tests a full clutch pack and, while giving an overall performance of the clutch/lubricant system, does not give detailed knowledge of friction characteristics or the influences of wear of the components.
The TE 92M Automated Clutch Friction Test Machine offers just that possibility. It uses a single friction pair in their original manufactured state. The machine may be configured to accept clutch plates from North American, European and Japanese manufacturers by fitting appropriate clamps TE 92M/FPC. Clutch plates up to 11.25 inch (286 mm) diameter may be accommodated.
The machine may also be used to test limited-slip differential, synchromesh and torque converter components with custom design modifications. The machine can be supplied with test adapters to conform to the JASO M349 standard.
Description
Motor and Test Spindle
The test spindle projects downwards from the machine top plate and runs in a housing with greased for life bearings. The drive motor is also mounted on the top plate and is connected to a pulley on the outer casing of a two-speed epicyclic gear-box, which is mounted on the test spindle. The lever selected gear ratios are 6:1 for low speeds and high torque tests on full-sized clutch plates and 1:1 for testing smaller diameter LVFA and thrust washer specimens.
An a.c. vector motor with encoder feedback provides precise speed control with a turn-down ratio of 1000:1. This is required for ramped speed sweep tests, with stable speed control down to zero rpm.
The COMPEND 2000 control system and data acquisition system with complex speed set point capability provides control of continuous ramps from zero up to the maximum speed as well as operation with discrete steps of speed.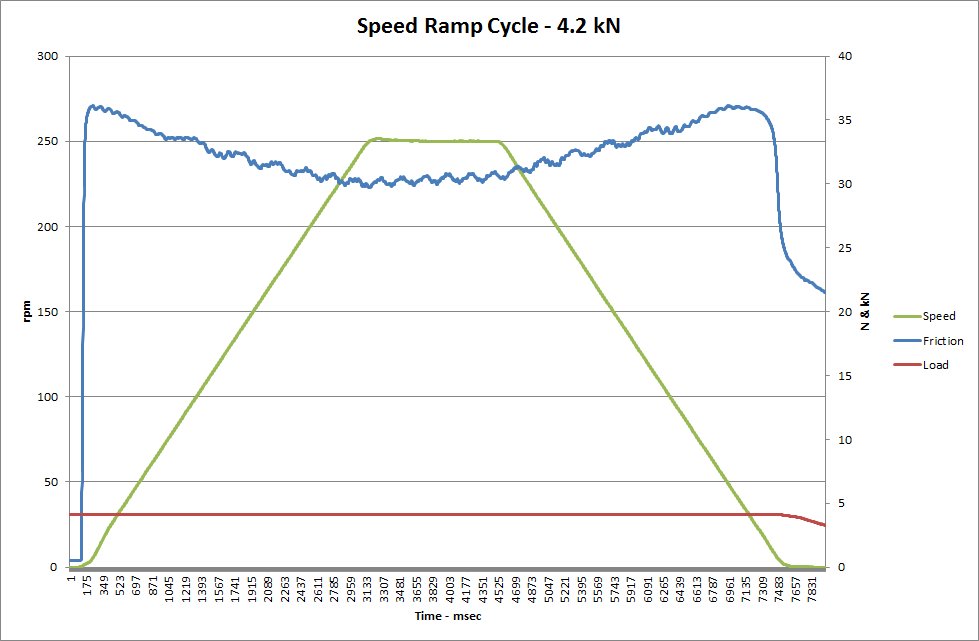
Load and Torque Measurement
Test baths are torque reaction mounted a spherical bearing, on an aluminium cross beam, which is mounted on linear bearings running on vertical columns. The beam is loaded from by a pneumatic bellows assembly with a force transducer for closed loop control of load. Stops are provided to allow the test components to be brought out of contact by removing the load to allow cyclic engagement and loading of clutch components.
Test Bath
The stationary specimen is mounted in test bath using a modular clamping system to accommodate a range of diameters and spline arrangements. Parts of the clamp are manufactured to suit the spline arrangements on the clutch plates.
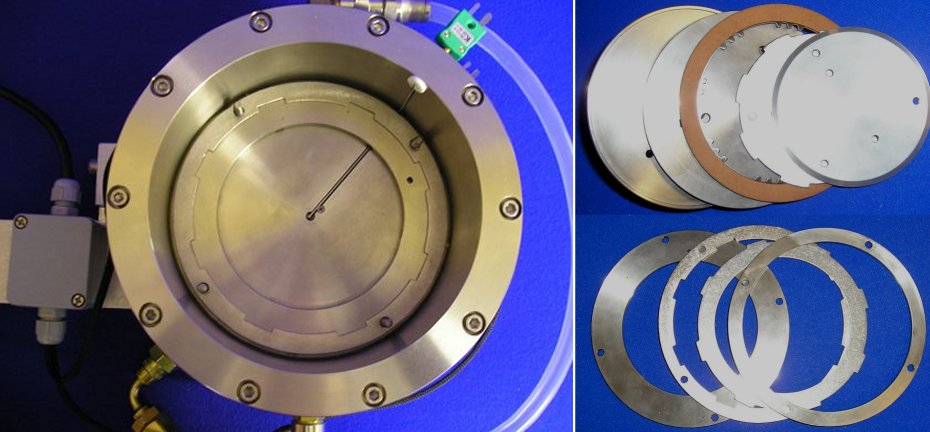
The test bath includes both cooling passages for removal of heat with cooling fluid during low temperature tests and resistance heaters for adding heat for high temperature tests.
Temperature sensors are provided to monitor the fluid temperature and the bottom surface of the stationary specimen.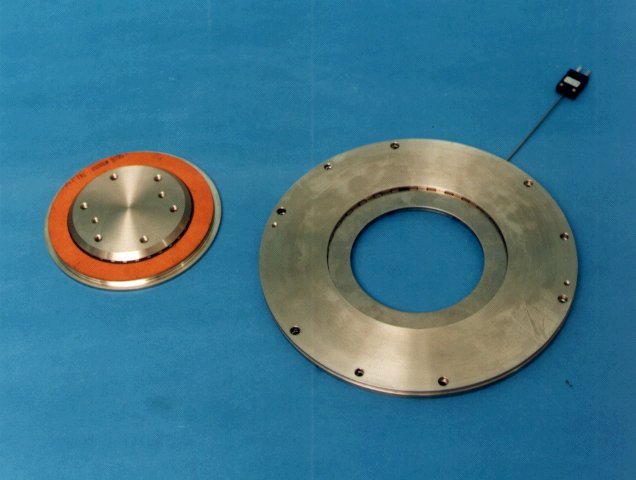
The rotating specimen is mounted on a flange using a modular clamping system to accommodate a range of diameters and spline arrangements. Parts of the clamp are manufactured to suit the spline arrangements on the rings.
Lubrication
A number of options are available for lubricating the contact, depending on the test work being carried out. The JASO standard requires the use of specific clutch components and an oil volume of 100 ml whereas other tests may use over 1 litre of fluid in the reservoir. Different reservoirs may be required to accommodate the required test specimens and fluid volumes.
Safety
All rotating parts are guarded for worker safety. A mechanical cut-off is also provided to protect the torque transducer from over-load.
The software incorporates Alarm Level checking features that are switchable from step to step to take account of changing load conditions. There are two types of alarm, for warning and for machine shutdown. For instance a friction coefficient may be used to shut down the machine in the case of over-torque events and temperature may be used in case of over temperature.Control and Data Acquisition
Control and data acquisition are implemented via host PC running COMPEND 2020 Windows compatible software, in conjunction with a Phoenix Tribology USB micro-controller interface.
Automatic control is implemented via user programmable test sequences. Manual control is implemented using on screen toggles. Data is stored to hard disc in either .csv or .tsv file formats. -
Technical Specifications
Specimen Size: Mean radius of friction material: 35 to 125 mm (typical) Maximum outer diameter: 286 mm Small Size Specimen: Mean radius of friction material: 15 mm (typical LVFA) Speed Turn-Down Ratio: 100:1 Machine Torque/Speed: 37.5 Nm @ 1,000 rpm 18.7 Nm @ 2,000 rpm 224 Nm @ 167 rpm 112 Nm @ 333 rpm 50% over-current capacity for 30 seconds Low Load: 50 to 1,000 N (LVFA specimens) High Load: 250 to 10,000 N (CLUTCH specimens) Torque Transducer: strain gauge beam Range: 1,000 N Torque Arm Radius: 187 mm Torque Range: 180 Nm Heater Power: 3 kW Method: electrical resistance heaters Temperature Range: 40 to 200°C (100 to 400°F) Temperature Sensor: K-type thermocouple Motor: 4 kW, 4-pole ac with 1024 pulse per rev shaft encoder Interface: Serial Link Interface Module Software: COMPEND 2000 TE 92M/CSM Coolant Service Module Circulating Fluid: heat transfer oil Feed Pump: positive displacement gear pump Pump Power: 0.37 kW Flow Rate: 4 litres/minute maximum Control Valve: 3-way electro-pneumatic Controlled Parameters Rotational Speed Temperatures Load Test Duration Recorded Parameters Load Rotational Speed Friction Torque Temperatures Test Duration Friction Coefficient Services Electricity: 380/415 V, three phase, 50/60 Hz, with neutral and earth 7.5 kW Clean, dry air: 4 cfm at 8 bar (120 psi) Mains water and drain: 10 l/min (typical) Installation Floor-standing machine: 600 mm x 800 mm deep x 1,000 mm high, 400 kg Coolant service module: 930 mm x 530 mm x 500 mm high, 50 kg -
Index Tags
automatic transmission fluids clutch friction clutch lubricants clutch materials friction materials LVFA testing special applications stick-slip torque converter components -

